
Historical Context: The Rise of Reefer Madness
To understand the current societal views on hemp and marijuana, it is essential to explore the historical backdrop to what contributed to their distinct perceptions. In the early 20th century, the United States witnessed a significant shift in attitudes towards cannabis, which was largely influenced by sensationalist media and political maneuvering. The term “Reefer Madness” which originates from the 1936 propaganda film “Reefer Madness” became cornerstone of this campaign. Led by figures like Harry J. Anslinger, the first commissioner of the Federal Bureau of Narcotics, and supported by media mogul William Randolph Hearst, this agenda aimed at demonizing marijuana by exaggerating its purported dangers and presenting it as a catalyst for societal decay.

During this period, a series of events led to the stigmatization of both hemp and marijuana. Although hemp had been cultivated for centuries for its versatile applications, including textile production and industrial uses, the emergence of the cannabis prohibition movement overshadowed its benefits. As marijuana gained notoriety through its association with jazz culture and immigrant communities, fears about its influence on social order began to rise. These fears were fueled by sensationalist media campaigns and political rhetoric, which ultimately led to the passage of the Marihuana Tax Act of 1937. This act introduced stringent regulations that severely restricted cannabis cultivation, effectively pushing both hemp and marijuana into the shadows of legality.
The misinformation propagated during the Reefer Madness era fostered a cultural climate filled with stigma and misunderstanding. As a result, hemp, which possesses numerous economic and environmental advantages, faced unjust criminalization alongside its psychoactive counterpart. This misrepresentation not only impacted public perception but also masked the potential of hemp, leaving many of its valuable uses unexplored for decades. Moreover, the division between hemp and marijuana deepened, with each being relegated to separate narratives fueled by fear rather than fact.
Ultimately, the legacy of Reefer Madness laid the groundwork for the ongoing complexities surrounding hemp and marijuana. As society progresses towards better understanding and acceptance, it becomes crucial to reflect on these historical contexts that shaped modern views and policies surrounding these two cannabis plants.
Industrial Uses: Hemp vs. Marijuana

The industrial applications of hemp and marijuana illustrate the significant differences between these two cannabis species. Hemp, known for its sustainability and versatility, is utilized across various industries, including textiles, construction, food, and biofuels. The fibers derived from hemp plants are exceptionally strong and durable, making them an ideal material for fabrics, ropes, and composites. In the textile industry, hemp canvas has been favored for its breathability and resistance to mold and mildew, making it suitable for various applications, including clothing and accessories.
In the construction sector, hempcrete, a mixture of hemp hurds and lime, is gaining attention as an eco-friendly building material. This composite provides excellent insulation properties while being lightweight and resilient. Additionally, hemp seeds and oil are increasingly utilized in the food industry. From nutritious hemp seeds to hemp oil rich in omega fatty acids, these products have gained popularity among health-conscious consumers. Furthermore, hemp biomass can be transformed into biofuels, contributing to sustainable energy solutions and reducing carbon footprints.

In stark contrast, the primary industrial use of marijuana lies in its medicinal and recreational applications. The presence of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in marijuana bestows psychoactive properties that contribute to its use in alleviating pain, reducing anxiety, and providing therapeutic benefits for various medical conditions. As societal perceptions shift and policies around cannabis evolve, the demand for marijuana products has exploded within both the healthcare and recreational sectors.
In summary, while hemp serves a multitude of industrial purposes that emphasize its sustainability and practicality, marijuana’s role is largely defined by its psychoactive effects and medicinal benefits. This distinction underlines the unique contributions of each plant to society while clarifying their specific applications across various industries.
Cannabinoid Composition: Hemp vs. Marijuana
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds found in both hemp and marijuana that interact with the endocannabinoid system in the human body. The two most widely recognized cannabinoids are cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). These compounds play a significant role in defining the characteristics and classifications of hemp and marijuana, which differ primarily in their cannabinoid profiles.
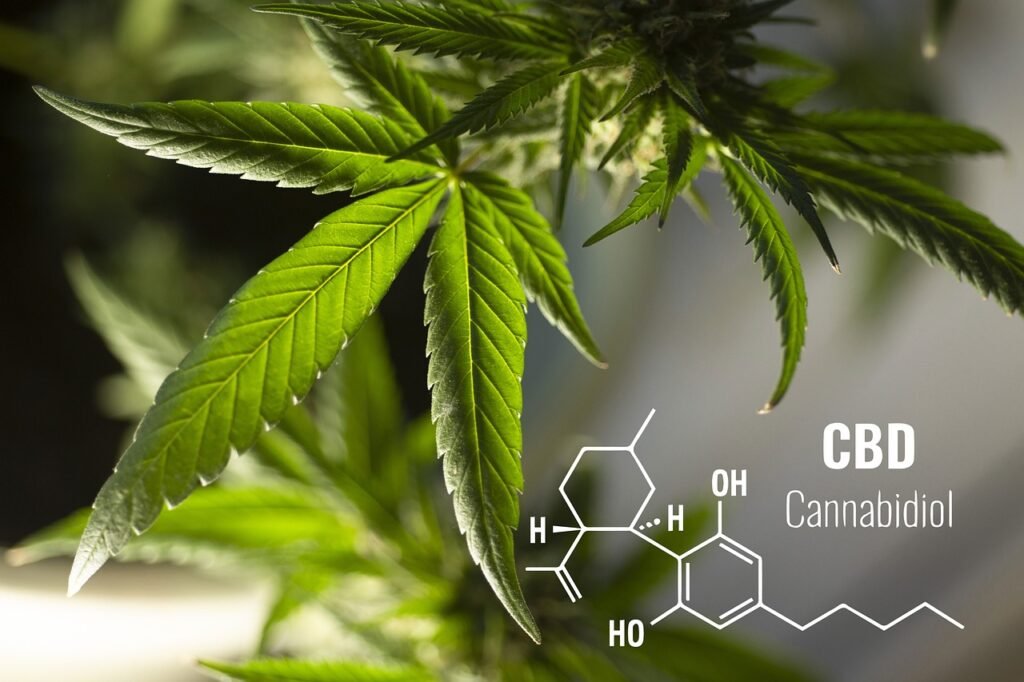
Hemp typically contains a high concentration of CBD and low levels of THC, generally below 0.3%. This low THC content means that hemp does not produce the psychoactive effects commonly associated with marijuana use. CBD is known for its various therapeutic benefits, such as reducing inflammation, alleviating anxiety, and managing pain without inducing a “high.” Hemp-based products, including oils and capsules, have gained popularity in wellness and alternative medicine for these properties.

Conversely, marijuana is characterized by higher concentrations of THC, often exceeding 20%. THC is the psychoactive component that creates the euphoric sensation sought by many users. This compound can also produce potential therapeutic benefits, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and relaxation. However, the legal status of marijuana varies by region due to its psychoactive properties, which complicates its use in both recreational and medical contexts.
In summary, the core differences in cannabinoid composition between hemp and marijuana—namely CBD and THC levels—are pivotal in determining their usage and legal implications. While hemp is primarily utilized for its non-psychoactive benefits, marijuana is sought after for its psychoactive effects and therapeutic potential. Understanding these differences is essential for both consumers and researchers as they navigate the evolving landscape of cannabinoid-based products.
Legal Landscape: Hemp vs. Marijuana

While hemp has been classified under the same schedule as Marijuana for quite some time, the 2018 Farm Bill changed that by removing hemp from the Controlled Substances Act (CSA), making it legal to grow, process, and sell hemp and its derivatives, including CBD, as long as the THC content does not exceed 0.3%. Marijuana, however, remains a Schedule I controlled substance under the CSA, indicating a high potential for abuse and no current accepted medical use. However, some states have legalized marijuana for medical or recreational purposes, creating a conflict between federal and state laws.
Despite the progress made in legal recognition, stigma associated with marijuana use persists. Historical narratives and cultural perceptions frequently frame marijuana in a negative light, affecting public sentiment and policy decisions. This ongoing stigma can lead to challenges for consumers seeking marijuana for therapeutic purposes and for businesses operating in this space. Industry advocates are working to promote awareness and understanding of the benefits associated with responsible marijuana use, highlighting the distinctions between hemp and marijuana.

Ultimately, navigating the contrasting landscapes of hemp and marijuana requires a nuanced perspective, acknowledging both the advancements in legalization and the lingering societal challenges. As attitudes continue to evolve, it is crucial to recognize the complex interplay between legal frameworks, public perception, and the economic implications of these differences. Engaging in informed discussions about the legal distinctions between hemp and marijuana is vital for everyone involved in this space. These conversations can help address ongoing stigmas, clarify regulatory complexities, and foster a more informed and supportive community.

